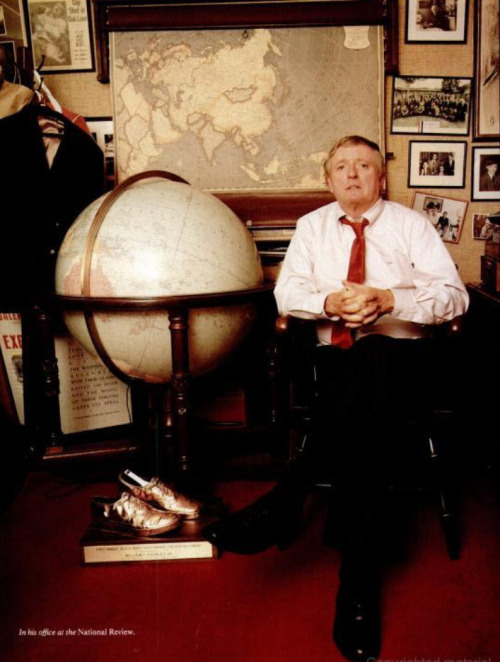
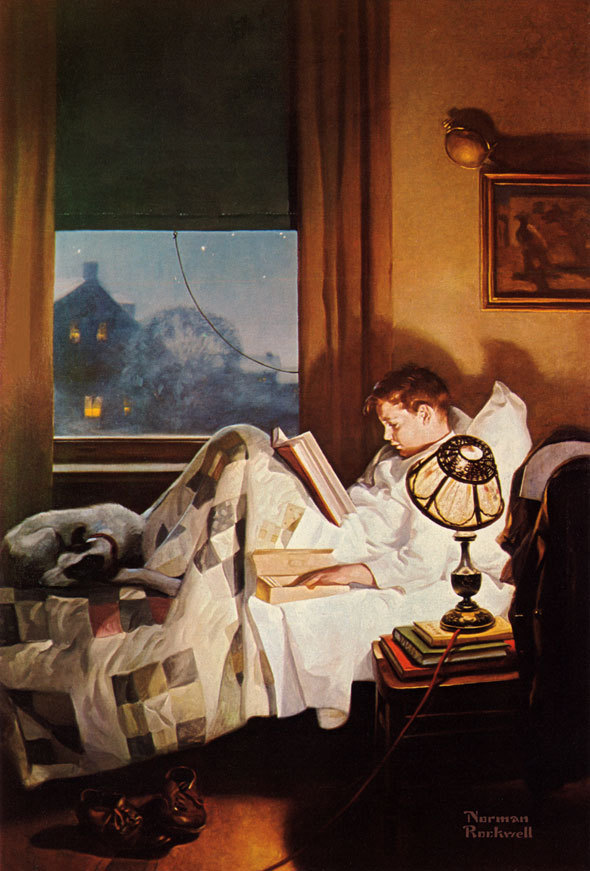
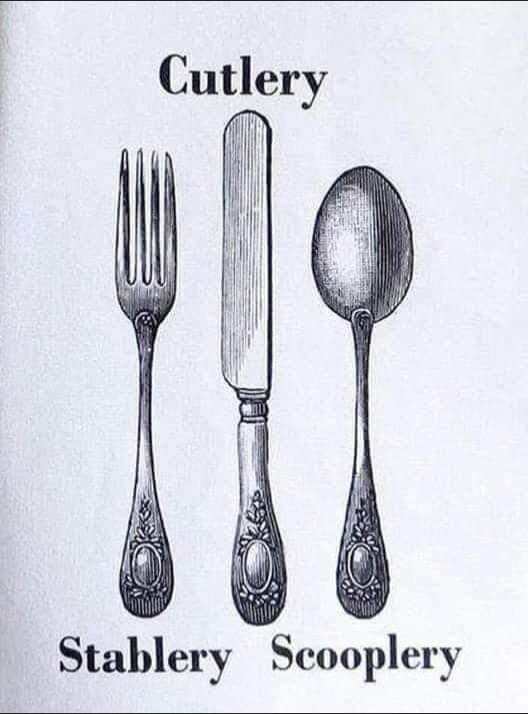
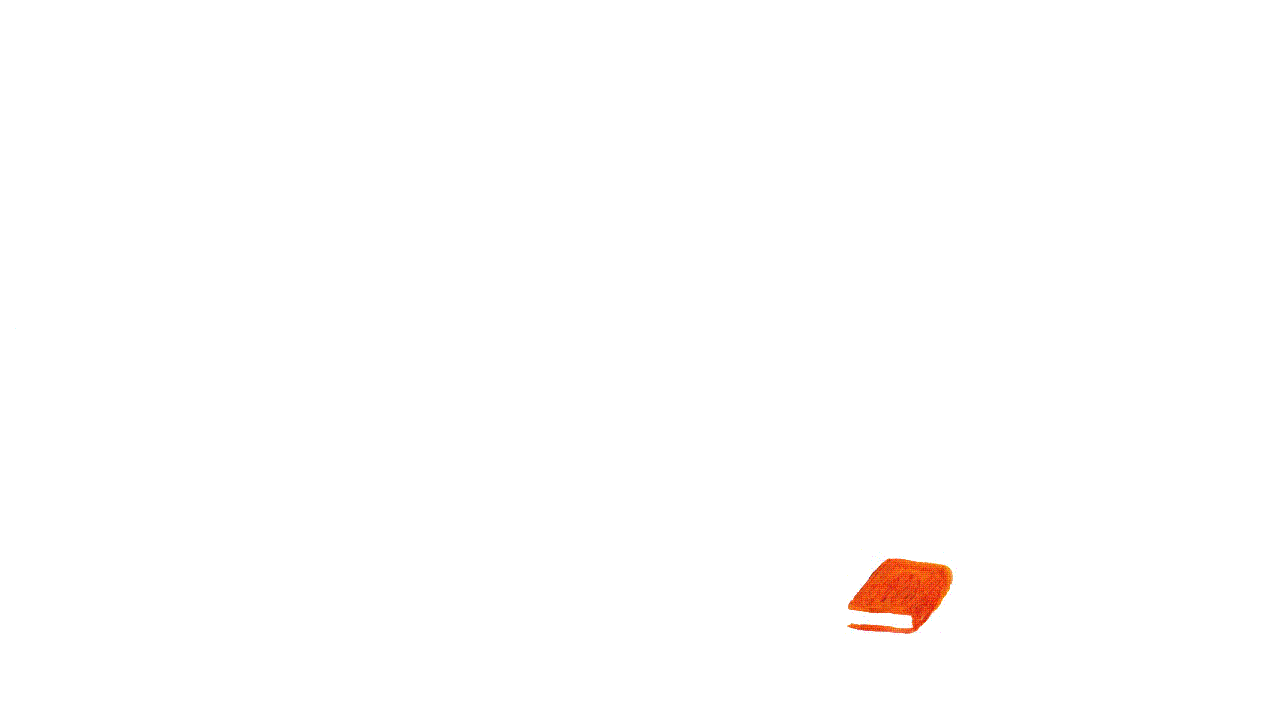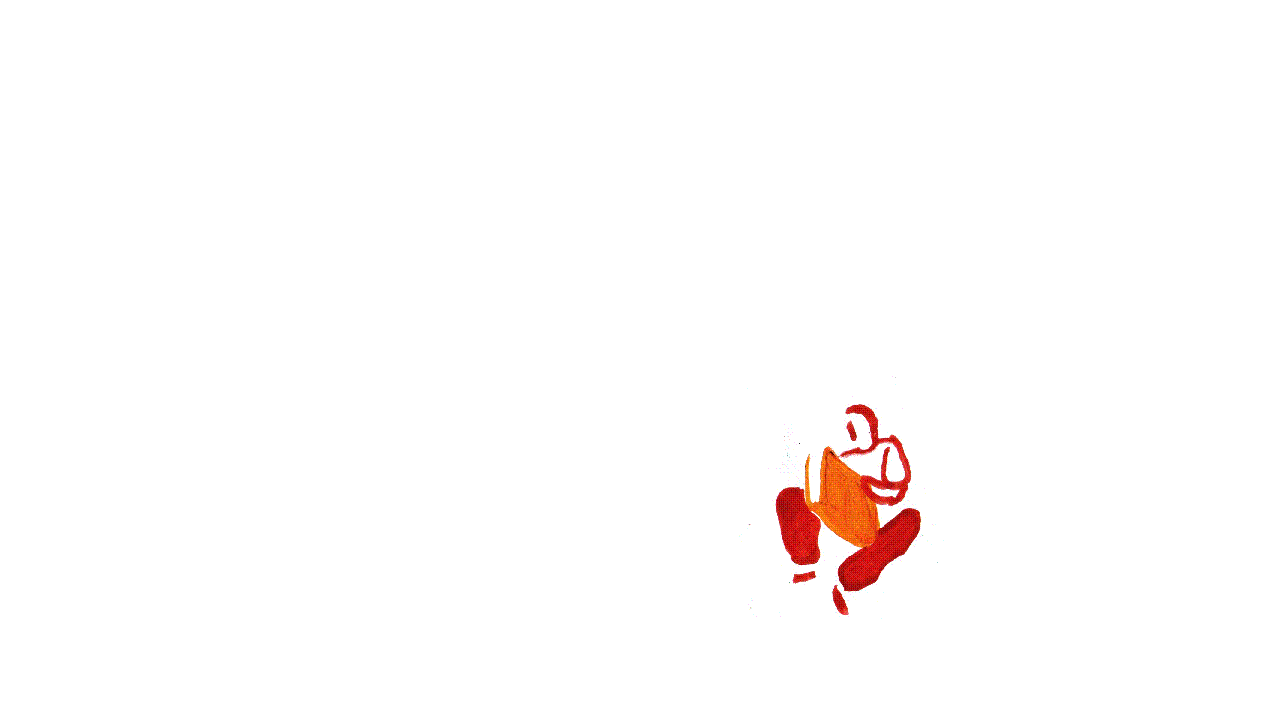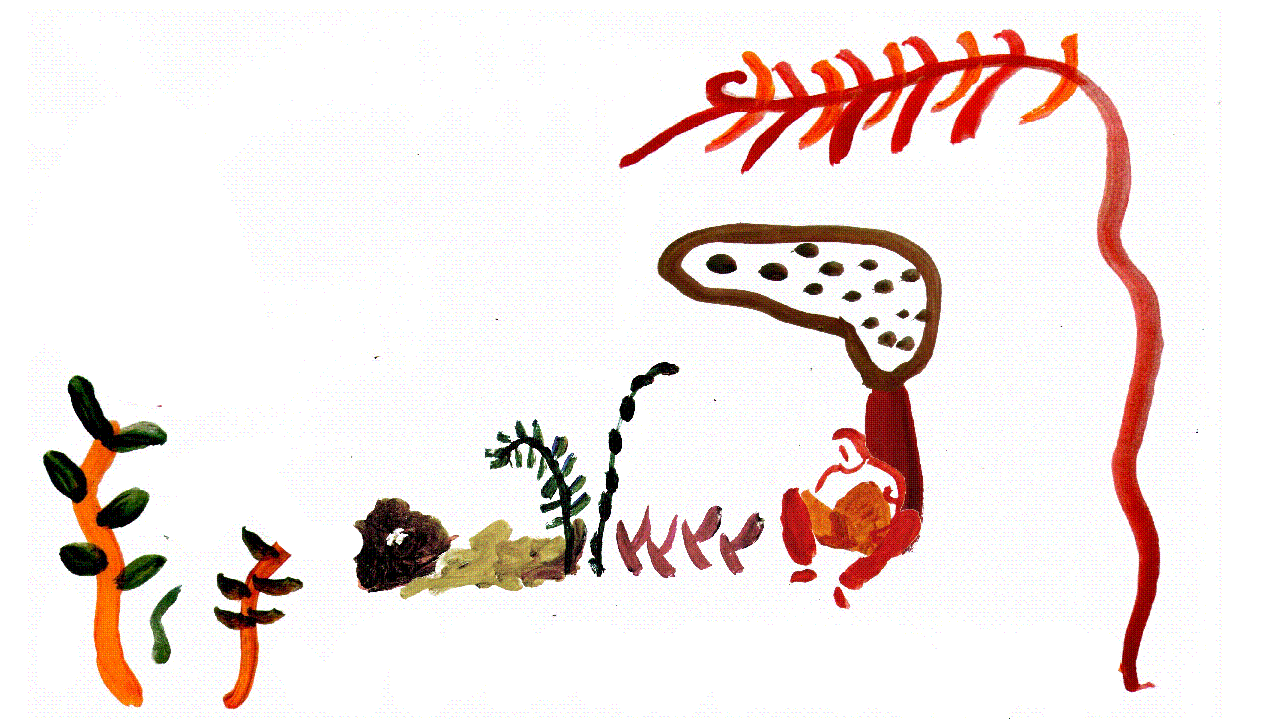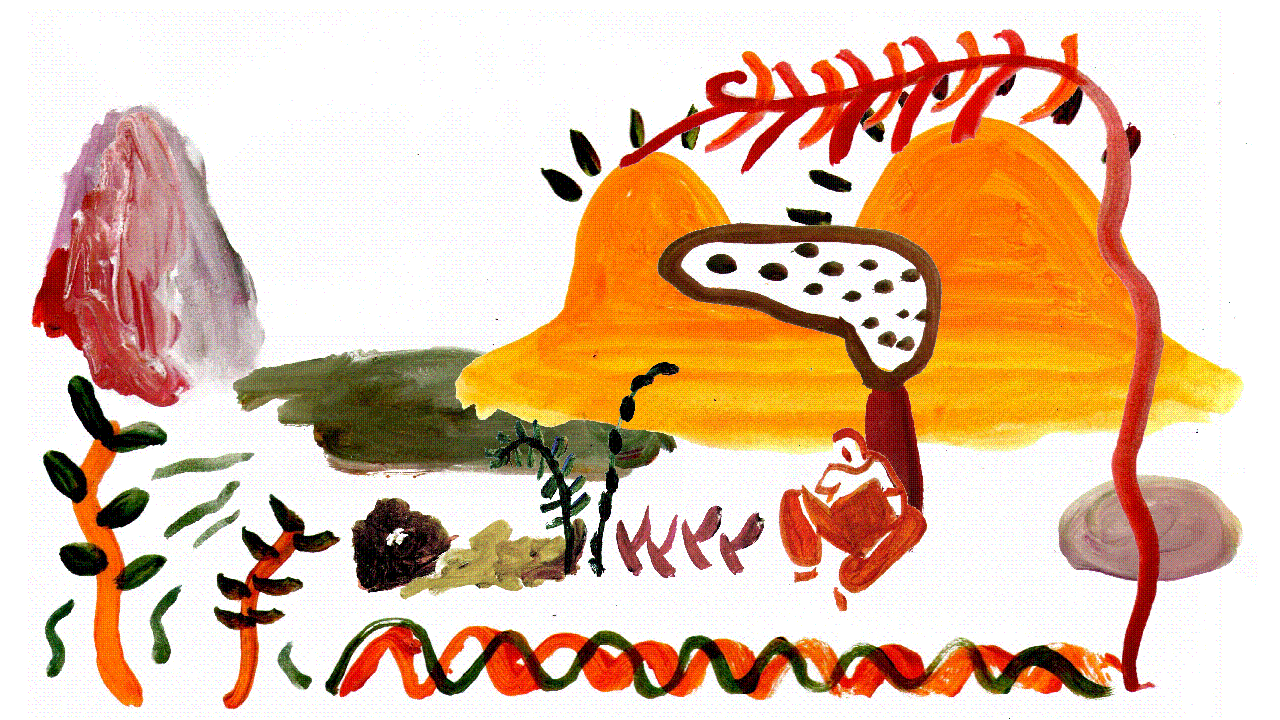
Gass, Lewis & Clark Holding a Council with the Indians, 1817
Jefferson had been trying to mount a western expedition of exploration since the 1790s, and his determination to do so had only grown since he became president in 1801. In summer 1802, Jefferson began actively preparing for the mission, recruiting his young personal secretary, Meriwether Lewis, to be its leader. Throughout 1802, Jefferson and Lewis discussed the proposed mission, telling no one-not even Congress, which would have to approve the funds-of what they were contemplating. Jefferson directed Lewis to draw up an estimate of expenses.
Basing his calculations on a party of one officer and 10 enlisted men-the number was deliberately kept small to avoid inspiring both congressional criticisms and Indian fears of invasion-Lewis carefully added up the costs for provisions, weapons, gunpowder, scientific instruments, and a large boat. The final tally came to $2,500. The largest item was $696, earmarked for gifts to Indians.
Following the advice of his secretary of the treasury, Albert Gallatin, Jefferson decided not to include the request in his general proposed annual budget, since it involved exploration outside of the nation’s own territory. Instead, on January 18, 1803, he sent a special secret message to Congress asking for the money, taking pains to stress that the proposed exploration would be an aid to American commerce. Jefferson noted that the Indians along the proposed route of exploration up the Missouri River “furnish a great supply of furs & pelts to the trade of another nation carried on in a high latitude.”
If a route into this territory existed, “possibly with a single portage, from the Western ocean,” Jefferson suggested Americans might have a superior means of exploiting the fur trade.
Though carefully couched in diplomatic language, Jefferson’s message to Congress was clear: a U.S. expedition might be able to steal the fur trade from the British and find the long hoped-for Northwest passage to the Pacific. Despite some mild resistance from Federalists who never saw any point in spending money on the West, Jefferson’s carefully worded request prevailed, and Congress approved the $2,500 appropriation by a sizeable margin. It no doubt seemed trivial in comparison to the $9,375,000 they had approved a week earlier for the Louisiana Purchase, which brought much of the territory Jefferson was proposing to explore under American control. With financing now assured, Lewis immediately began preparing for the expedition. Recruiting his old military friend, William Clark, to be his co-captain, the Corps of Discovery departed on their epic exploration of the uncharted regions in spring 1804.
Thanks to This Day in U.S. Military History.































































































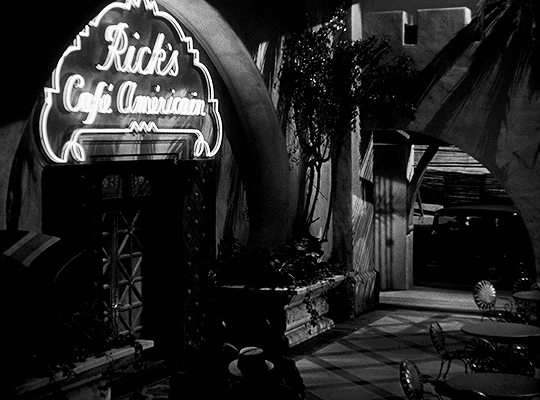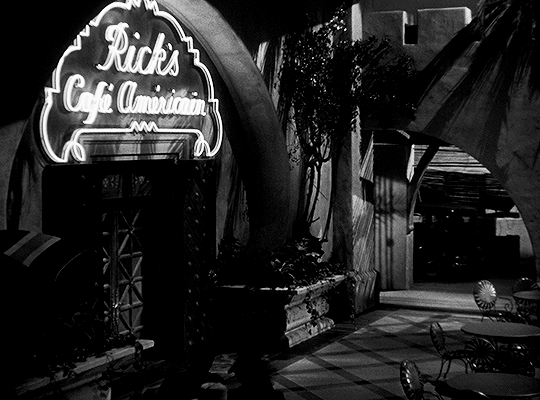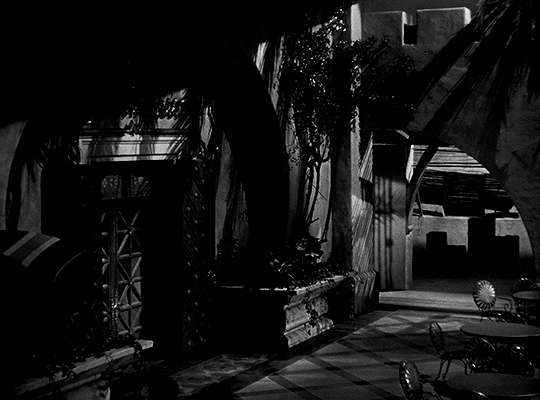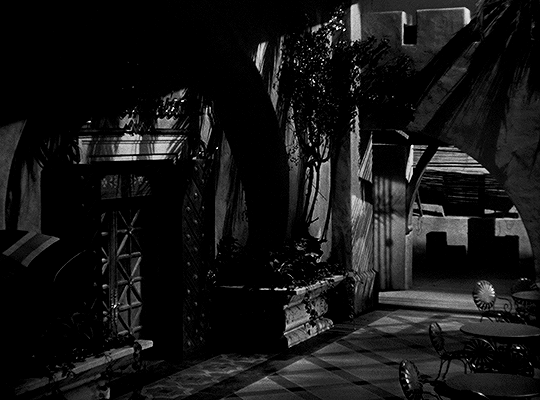









































































No comments:
Post a Comment