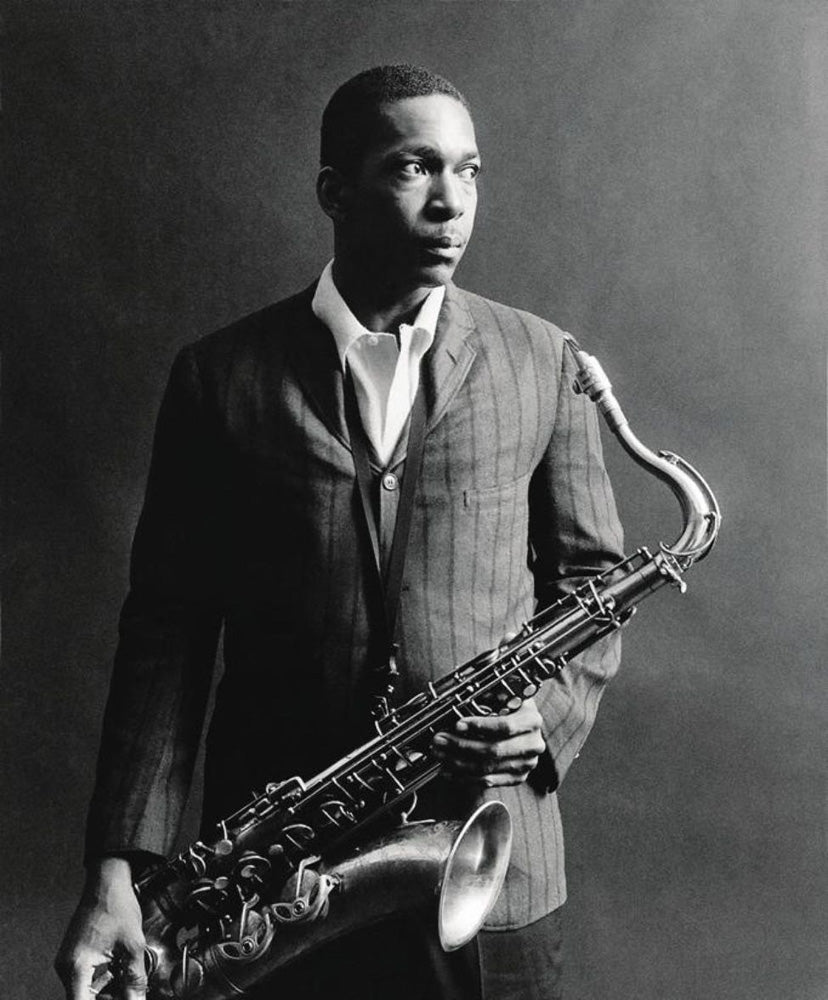
If the October days were a cordial like the sub-acids of fruit, these are a tonic like the wine of iron. Drink deep or be careful how you taste this December vintage. The first sip may chill, but a full draught warms and invigorates.
John Burroughs
A forest of things.
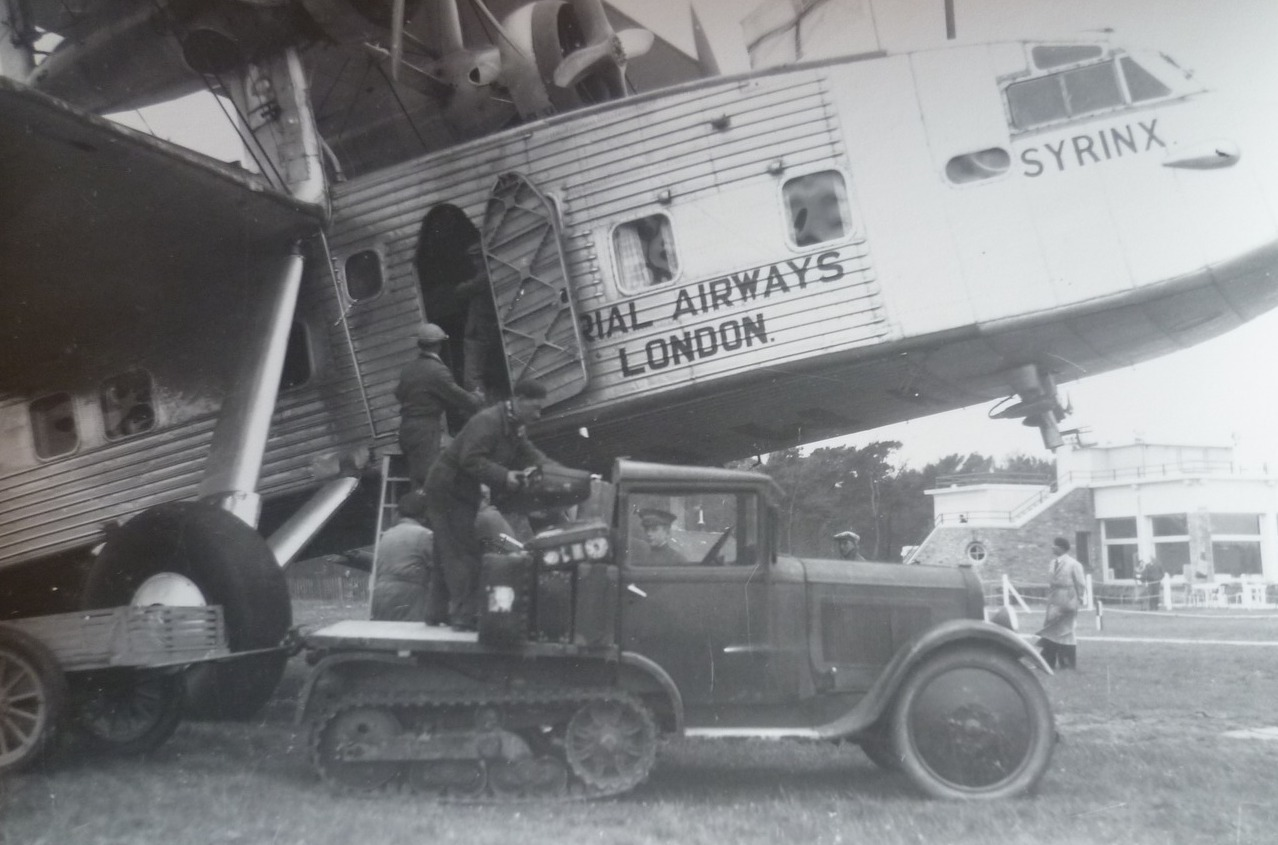
A healthy writing habit led to a culture of readers. Starting in the Middle Ages, Icelanders practiced something called the kvoldvaka (roughly, “night vigil”) in old farmsteads. During the long, dark, harsh winters, poor farmers huddled together in a single room in their turf houses to stay warm. “The kvoldvaka was the time between 6 and 10 p.m., roughly, when people would do their indoor work during the winter,” explains Alda Sigmundsdóttir, a writer and the founder of Little Books Publishing in Reykjavík. “They’d do their knitting, they’d make their tools, they’d work the wool—and during this session, there would be one person appointed to read to everyone else.”In those evening hours, children learned to tell, recite and read stories (teaching children to read, in fact, was required by both the church and the government). As Tomasson noted in “The Literacy of the Icelanders,” by the end of the grueling 18th century—when a smallpox epidemic killed as much as a third of the population and a volcanic eruption that lasted for eight months killed another fifth of the population and most of the livestock—nearly every surviving Icelander could read.Prior to the 20th century, “Christmas gifts used to be something useful, such as clothes or extra food,” says librarian Ingibjörg Steinunn Sverrisdóttir at the National and University Library of Iceland. Modern, international conflict would usher in new holiday traditions.The Jólabókaflóð traces back to Iceland’s transformation in World War II. In 1944, Iceland was a newly independent nation with a beleaguered wartime economy and 15,000 occupying Allied troops. “Because of the bad economy and depression, there were quotas or very strict restrictions on many things you could import,” says Heiðar Ingi Svansson, president of the Icelandic Publishers Association, an organization founded in 1889 that oversees the industry, promotes literature and awards annual literary prizes (announced each December and presented by the president of Iceland each January). “And that limited very much the selection of commodity goods that you could choose as Christmas gifts. But paper was one of the few commodities not rationed during the war—so paper was imported to produce books that were written and then printed in Iceland.” That fortuitous supply—and an infusion of occupation-related money—dovetailed beautifully with Icelanders’ literary leanings.
Good King Wenceslas looked out
On the Feast of Stephen...
The Druids started it. Mistletoe, a hemi-parasitic plant that grows on trees, has long been considered a cure-all with special properties: In the Aeneid, the hero brings a bough thought to be mistletoe—a symbol of vitality that remains green even in winter—to the underworld. But the earliest mention of mistletoe's romantic powers was by Roman natural historian Pliny the Elder, who scoffed at the Druids of the 1st Century A.D. for believing that "mistletoe, taken in drink, will impart fecundity to all animals that are barren." That romantic association was later expanded by the Norse myth about Baldur and his mother, Frigga, the goddess of love and marriage. According to legend, Frigga got all the plants and animals of the Earth to promise not to harm her son—except mistletoe. Loki, the god of mischief, took that opportunity to kill Baldur with a spear made of mistletoe. In some versions of the tale, Frigga's tears then turned into mistletoe berries, which brought Baldur back to life, prompting Frigga to declare mistletoe a symbol of love.In his essay on Christmas Eve, Washington Irving vividly describes the proper setting ...
As we approached the house we heard the sound of music, and now and then a burst of laughter from one end of the building. This, Bracebridge said, must proceed from the servants' hall, where a great deal of revelry was permitted, and even encouraged, by the squire throughout the twelve days of Christmas, provided everything was done conformably to ancient usage. Here were kept up the old games of hoodman blind, shoe the wild mare, hot cockles, steal the white loaf, bob apple, and snap dragon; the Yule-clog and Christmas candle were regularly burnt, and the mistletoe with its white berries hung up, to the imminent peril of all the pretty housemaids. The mistletoe is still hung up in farm-houses and kitchens at Christmas, and the young men have the privilege of kissing the girls under it, plucking each time a berry from the bush. When the berries are all plucked the privilege ceases.
But no human being can be trusted to keep his or her word when he or she has access to power—a power not available to opponents.
Dr. Frankl would remind us ...
Between stimulus and response there is a space. In that space is our power to choose our response. In our response lies our growth and freedom.
What power is truly eluding you?
A World War II fighter ace and Medal of Honor recipient, Col. "Pappy" Boyington (1912-1988) shot down a total of 28 Japanese aircraft during his wartime service. Initially in Army ROTC, he joined the Marine Corps in 1935. In August 1941, however, he resigned his Marine commission in order to join the Flying Tigers (1st American Volunteer Group), organized by Gen. Claire Chennault to assist the Chinese Air Force. Boyington rejoined the Marines in 1942 and commanded the "Black Sheep" squadron (Marine Fighting Squadron 214) in the South Pacific. On January 3, 1944, he was shot down, captured and then held in a Japanese prison camp for 20 months. Boyington's 1958 memoir, "Baa Baa Black Sheep," inspired the 1970s television series of the same name.Medal of Honor citation:"For extraordinary heroism and valiant devotion to duty as commanding officer of Marine Fighting Squadron 214 in action against enemy Japanese forces in the Central Solomons area from 12 September 1943 to 3 January 1944. Consistently outnumbered throughout successive hazardous flights over heavily defended hostile territory, Maj. Boyington struck at the enemy with daring and courageous persistence, leading his squadron into combat with devastating results to Japanese shipping, shore installations, and aerial forces. Resolute in his efforts to inflict crippling damage on the enemy, Maj. Boyington led a formation of 24 fighters over Kahili on 17 October and, persistently circling the airdrome where 60 hostile aircraft were grounded, boldly challenged the Japanese to send up planes. Under his brilliant command, our fighters shot down 20 enemy craft in the ensuing action without the loss of a single ship. A superb airman and determined fighter against overwhelming odds, Maj. Boyington personally destroyed 26 of the many Japanese planes shot down by his squadron and, by his forceful leadership, developed the combat readiness in his command which was a distinctive factor in the Allied aerial achievements in this vitally strategic area."
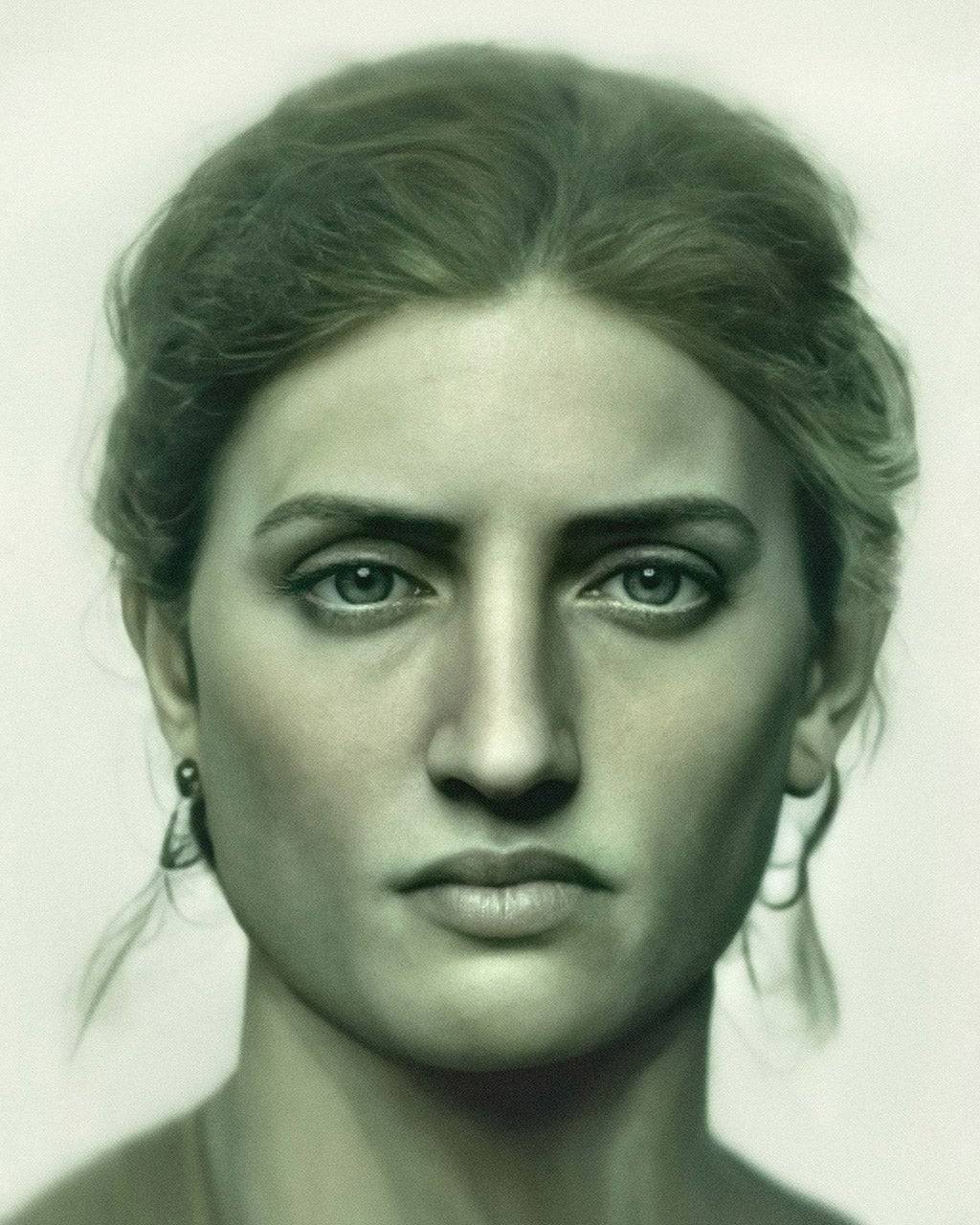
As a portraitist, the garrulous Stuart had perfected a technique to penetrate his subjects’ defenses. He would disarm them with a steady stream of personal anecdotes and irreverent wit, hoping that this glib patter would coax them into self-revelation. In the taciturn George Washington, a man of granite self-control and a stranger to spontaneity, Gilbert Stuart met his match. From boyhood, Washington had struggled to master and conceal his deep emotions. When the wife of the British ambassador later told him that his face showed pleasure at his forthcoming departure from the presidency, Washington grew indignant: “You are wrong. My countenance never yet betrayed my feelings!” He tried to govern his tongue as much as his face: “With me it has always been a maxim rather to let my designs appear from my works than by my expressions.”
When Washington swept into his first session with Stuart, the artist was awestruck by the tall, commanding president. Predictably, the more Stuart tried to pry open his secretive personality, the tighter the president clamped it shut. Stuart’s opening gambit backfired. “Now, sir,” Stuart instructed his sitter, “you must let me forget that you are General Washington and that I am Stuart, the painter.” To which Washington retorted drily that Mr. Stuart need not forget “who he is or who General Washington is.”
A master at sizing people up, Washington must have cringed at Stuart’s facile bonhomie, not to mention his drinking, snuff taking, and ceaseless chatter. With Washington, trust had to be earned slowly, and he balked at instant familiarity with people. Instead of opening up with Stuart, he retreated behind his stolid mask. The scourge of artists, Washington knew how to turn himself into an impenetrable monument long before an obelisk arose in his honor in the nation’s capital.
As Washington sought to maintain his defenses, Stuart made the brilliant decision to capture the subtle interplay between his outward calm and his intense hidden emotions, a tension that defined the man. He spied the extraordinary force of personality lurking behind an extremely restrained facade. The mouth might be compressed, the parchment skin drawn tight over ungainly dentures, but Washington’s eyes still blazed from his craggy face. In the enduring image that Stuart captured and that ended up on the one-dollar bill—a magnificent statement of Washington’s moral stature and sublime, visionary nature—he also recorded something hard and suspicious in the wary eyes with their penetrating gaze and hooded lids.
With the swift insight of artistic genius, Stuart grew convinced that Washington was not the placid and composed figure he presented to the world. In the words of a mutual acquaintance, Stuart had insisted that “there are features in [Washington’s] face totally different from what he ever observed in that of any other human being; the sockets of the eyes, for instance, are larger than he ever met with before, and the upper part of the nose broader. All his features, [Stuart] observed, were indicative of the strongest and most ungovernable passions, and had he been born in the forests, it was his opinion that [Washington] would have been the fiercest man among the savage tribes.” The acquaintance confirmed that Washington’s intimates thought him “by nature a man of fierce and irritable disposition, but that, like Socrates, his judgment and great self-command have always made him appear a man of a different cast in the eyes of the world.